비전 프로 출시 D-2
Vision Pro Review: 24 Hours With Apple’s Mixed-Reality Headset | WSJ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8xI10SFgzQ8
실리콘밸리 시간으로는 3일, 한국시간으로는 2일 후 애플의 신형 디바이스인 비전 프로가 판매를 드디어 시작하는데요. 미국의 미디어와 유튜버들의 제품 리뷰와 영상이 본격적으로 공개되기 시작했어요. 유튜브나 뉴스검색을 통해서 찾아보실 수 있는데요. 리뷰어들의 소감 중에서 재미있는 것을 정리해봤어요.
- 무겁다 : 실제 무게도 있지만 메타 퀘스트와 달리 무게가 앞에 쏠려있는 점이 문제.
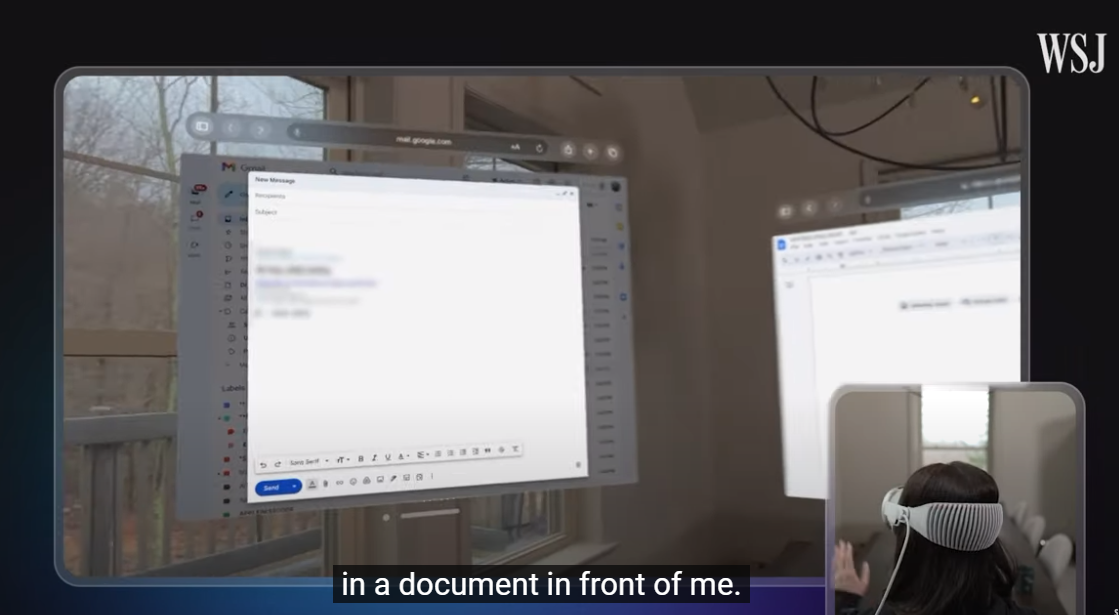
- 가상 키보드는 별로 : 비전 프로로 일을 하고 싶다면 실물 키보드를 추천.
- 안경은 못쓴다 : 안경을 쓰고 착용하기 어렵기 때문에 도수가 있는 렌즈를 별도로 구매해서 부착해야해요.
- 놀라운 디스플레이 : 디스플레이 성능이 너무 좋은데 이것이 높은 가격의 가장 큰 원인 중 하나.
- 패스스루도 완벽 : 비전 프로를 착용해도 카메라를 통해서 외부를 보는 혼합현실(Mixed Reality)기능이 매우 훌륭하다고 해요.
- 시리를 많이 사용하게 된다 : 음성 AI 비서인 시리가 비전프로에서도 당연히 작동을 하는데, 비전프로를 쓰고 있는 환경에서는 자연스럽게 시리를 호출해서 명령을 내리는 경우가 많아요. 마치 아이언맨이 자비스를 부르는 것 처럼요.
- 3D 영상 촬영이 킬러 서비스 : 아이폰15 프로로 공간동영상(Spatial)을 촬영할 수 있는데, 이걸 비전 프로에서 볼 수 있어요. 많은 리뷰어들이 여기에 만족을 나타냈어요. 2D 영상을 보는 것보다 과거의 경험을 다시 생생하게 느낄 수 있다고 해요. 특히 아이의 영상을 찍은 부모들의 만족도가 높았어요. 과거 캠코더가 아이들의 영상을 찍기 위해 많은 부모들이 샀던 것처럼 비전 프로 수요도 있을 것 같아요.
- 침대에 누워서 쓰기 좋다 : 침대에서 스마트폰을 쓰는 분들이 많은데, 비전 프로를 쓰면 무게도 덜 느끼고 좋을 것 같아요.
패스스루는 VR 화면에서 벗어나 주변의 실제 환경을 볼 수 있게 해주는 기능입니다. 패스스루는 헤드셋의 센서를 사용하여 사용자가 헤드셋 너머의 실제 환경을 본다고 가정했을 때 보게 될 환경을 대략적으로 보여줍니다. 안전 보호 경계를 만들거나 조정할 때 자동으로 패스스루가 작동합니다. 실제 및 가상 환경을 혼합하기 위해 앱에도 패스스루가 표시됩니다.
'프로그래밍 > Style & Design' 카테고리의 다른 글
| UI/UX Case Study: The Starbucks App Revamp You’ve All Been Waiting For… (0) | 2024.05.28 |
|---|---|
| 58 rules for beautiful UI design (0) | 2024.05.17 |
| 10 Powerful CSS Properties that Every Web Dev must know (0) | 2023.08.29 |
| [ICON] ion-icon 아이콘 사용하기 (0) | 2023.08.24 |
| [CSS] Magic inspired Social Share Button (0) | 2023.08.24 |





